Internet Key Exchange or IKE Is used by IPsec to establish security parameters between two sites. IKE allows us to exchange keys securely used for encryption and authentication over the internet. In the previous blog we discussed KE click here
IKEv2 phase 2 is also
known as child mode. the IKEv2 initiator sends a CREATE_CHILD_SA request, containing
a list of acceptable proposals for the child SA.
R3#show crypto ikev2 session
IPv4 Crypto IKEv2 Session
1 192.168.31.1/500 192.168.123.1/500 none/none READY
Encr: 3DES, Hash: SHA96, DH Grp:5, Auth sign: PSK, Auth verify: PSK
Life/Active Time: 86400/2923 sec
Child sa: local selector 192.168.30.0/0 - 192.168.30.255/65535
remote selector 192.168.10.0/0 - 192.168.10.255/65535
ESP spi in/out: 0xCF0FA2FE/0x5AAC2F32
The attributes that can be
negotiated include the following:
Protocol (AH 0r ESP)
Encapsulation mode (tunnel
or transport)
Encryption algorithm (for
example DES,3DES, or AES)
Authentication algorithm
(for example, HMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA)
Diffle-hellman group
information (for example, group 1, group 2, group 5, or group 14)
CLICK HERE FOR MORE TO LEARN
For gns3 IKEv2 supported
in IOS 15.1.1t
- IKEv2 supports many types of VPN
- GRE with IPsec
- SVTI.DVTI
- DMVPN
- GETVPN
- Interesting traffic (ACL)
- IKEv2 Proposal
- IKEv2 Policy
- IKEv2 Keyring
- IKEv2 Profile
- IPsec Transform set
- Crypto map
- Apply Map on an interface
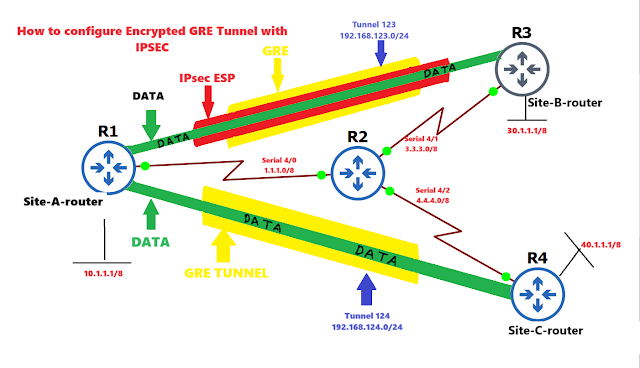
- Configure the topology as per the diagram
- Configure the IP addresses as per the topology
- Configure ACL and permit Fa0/0 traffic
- Configure IKEv2 Proposal
- Configure IKEv2 Policy
- Configure IKEv2 Keyring
- Configure IKEv2 Profile
- Configure Transform set
- Configure Crypto map
- Apply Crypto map on an interface
- verify with show commands and ping
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#no keepalive
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial 3/0
R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.123.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.31.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#ip route 192.168.30.0 255.255.255.0 serial 3/1
R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.31.1 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0
R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config-if)#no keepalive
R3(config-if)#exit
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.30.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 52/59/72 ms
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 192.168.10.1 YES manual up up
Serial3/0 192.168.123.1 YES manual up up
R3(config)#do ping 192.168.10.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.10.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 52/64/76 ms
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 192.168.30.1 YES manual up up
Serial3/1 192.168.31.1 YES manual up up
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Interesting traffic (ACL)
R1(config-ext-nacl)# permit ip 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.30.0 0.0.0.255
R1(config-ext-nacl)#exit
Extended IP access list ACL-TRAFFIC
10 permit ip 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.30.0 0.0.0.255 (6 matches)
Extended IP access list ACL-TRAFFIC
10 permit ip 192.168.30.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 (9 matches)
IKEv2 Proposal
IKEv2 proposal MUST have atleast an encryption algorithm, an integrity algorithm and a dh group configured
R1(config-ikev2-proposal)# encryption 3des aes-cbc-128 aes-cbc-256
R1(config-ikev2-proposal)# integrity sha1 sha256 sha384 sha512
R1(config-ikev2-proposal)# group 5 2 14 15
R1(config-ikev2-proposal)#exit
R1(config)#exit
IKEv2 proposal: IKEV2-PROPOSAL
Encryption : 3DES AES-CBC-128 AES-CBC-256
Integrity : SHA96 SHA256 SHA384 SHA512
PRF : SHA1 SHA256 SHA384 SHA512
DH Group : DH_GROUP_1536_MODP/Group 5 DH_GROUP_1024_MODP/Group 2 DH_GROUP_2048_MODP/Group 14 DH_GROUP_3072_MODP/Group 15
IKEv2 proposal: default
Encryption : AES-CBC-256 AES-CBC-192 AES-CBC-128
Integrity : SHA512 SHA384 SHA256 SHA96 MD596
PRF : SHA512 SHA384 SHA256 SHA1 MD5
DH Group : DH_GROUP_1536_MODP/Group 5 DH_GROUP_1024_MODP/Group 2
IKEv2 proposal MUST have atleast an encryption algorithm, an integrity algorithm and a dh group configured
R3(config-ikev2-proposal)# encryption 3des aes-cbc-128 aes-cbc-256
R3(config-ikev2-proposal)# integrity sha1 sha256 sha384 sha512
R3(config-ikev2-proposal)# group 5 2 14 15
R3(config-ikev2-proposal)#exit
IKEv2 proposal: IKEV2-PROPOSAL
Encryption : 3DES AES-CBC-128 AES-CBC-256
Integrity : SHA96 SHA256 SHA384 SHA512
PRF : SHA1 SHA256 SHA384 SHA512
DH Group : DH_GROUP_1536_MODP/Group 5 DH_GROUP_1024_MODP/Group 2 DH_GROUP_2048_MODP/Group 14 DH_GROUP_3072_MODP/Group 15
IKEv2 proposal: default
Encryption : AES-CBC-256 AES-CBC-192 AES-CBC-128
Integrity : SHA512 SHA384 SHA256 SHA96 MD596
PRF : SHA512 SHA384 SHA256 SHA1 MD5
DH Group : DH_GROUP_1536_MODP/Group 5 DH_GROUP_1024_MODP/Group 2
IKEv2 Policy
IKEv2 policy MUST have atleast one complete proposal attached
R1(config-ikev2-policy)# proposal IKEV2-PROPOSAL
R1(config-ikev2-policy)#exit
R1(config)#
Match fvrf : global
Match address local : any
Proposal : IKEV2-PROPOSAL22
Match fvrf : any
Match address local : any
Proposal : default
IKEv2 policy MUST have atleast one complete proposal attached
R3(config-ikev2-policy)# proposal IKEV2-PROPOSAL
R3(config-ikev2-policy)#exit
Match fvrf : global
Match address local : any
Proposal : IKEV2-PROPOSAL
Match fvrf : any
Match address local : any
Proposal : default
IKEv2 Keyring
R1(config-ikev2-keyring)# peer R3
R1(config-ikev2-keyring-peer)# address 192.168.31.1
R1(config-ikev2-keyring-peer)# pre-shared-key local internet
R1(config-ikev2-keyring-peer)# pre-shared-key remote internet
R1(config-ikev2-keyring-peer)# exit
R1(config-ikev2-keyring)#exit
R3(config-ikev2-keyring)# peer R1
R3(config-ikev2-keyring-peer)# address 192.168.123.1
R3(config-ikev2-keyring-peer)# pre-shared-key local internet
R3(config-ikev2-keyring-peer)# pre-shared-key remote internet
R3(config-ikev2-keyring-peer)# exit
R3(config-ikev2-keyring)#exit
IKEv2 Profile
IKEv2 profile MUST have:
1. A local and a remote authentication method.
2. A match identity or a match certificate statement.
R1(config-ikev2-profile)#match identity remote address 192.168.31.1 255.255.255.255
R1(config-ikev2-profile)# authentication remote pre-share
R1(config-ikev2-profile)# authentication local pre-share
R1(config-ikev2-profile)# keyring local IKEV2-KEYRING
R1(config-ikev2-profile)#exit
Ref Count: 2
Match criteria:
Fvrf: global
Local address/interface: none
Identities:
address 192.168.31.1 255.255.255.255
Certificate maps: none
Local identity: none
Remote identity: none
Local authentication method: pre-share
Remote authentication method(s): pre-share
EAP options: none
Keyring: IKEV2-KEYRING
Trustpoint(s): none
Lifetime: 86400 seconds
DPD: disabled
NAT-keepalive: disabled
Ivrf: none
Virtual-template: none
AAA EAP authentication mlist: none
AAA Accounting: none
AAA group authorization: none
AAA user authorization: none
IKEv2 profile MUST have:
1. A local and a remote authentication method.
2. A match identity or a match certificate statement.
R3(config-ikev2-profile)#match identity remote address 192.168.123.1 255.255.255.255
R3(config-ikev2-profile)# authentication remote pre-share
R3(config-ikev2-profile)# authentication local pre-share
R3(config-ikev2-profile)# keyring local IKEV2-KEYRING
R3(config-ikev2-profile)#exit
Ref Count: 2
Match criteria:
Fvrf: global
Local address/interface: none
Identities:
address 192.168.123.1 255.255.255.255
Certificate maps: none
Local identity: none
Remote identity: none
Local authentication method: pre-share
Remote authentication method(s): pre-share
EAP options: none
Keyring: IKEV2-KEYRING
Trustpoint(s): none
Lifetime: 86400 seconds
DPD: disabled
NAT-keepalive: disabled
Ivrf: none
Virtual-template: none
AAA EAP authentication mlist: none
AAA Accounting: none
AAA group authorization: none
AAA user authorization: none
Transform-set
R1(cfg-crypto-trans)#exit
Transform set default: { esp-aes esp-sha-hmac }
will negotiate = { Transport, },
will negotiate = { Tunnel, },
R3(cfg-crypto-trans)#exit
Transform set default: { esp-aes esp-sha-hmac }
will negotiate = { Transport, },
will negotiate = { Tunnel, },
Crypto Map
% NOTE: This new crypto map will remain disabled until a peer
and a valid access list have been configured.
R1(config-crypto-map)# set peer 192.168.31.1
R1(config-crypto-map)# set transform-set TRANS-set
R1(config-crypto-map)# set ikev2-profile IKEV2-PROFILE
R1(config-crypto-map)# match address ACL-TRAFFIC
R1(config-crypto-map)#exit
% NOTE: This new crypto map will remain disabled until a peer
and a valid access list have been configured.
R3(config-crypto-map)# set peer 192.168.123.1
R3(config-crypto-map)# set transform-set TRANS-set
R3(config-crypto-map)# set ikev2-profile IKEV2-PROFILE
R3(config-crypto-map)# match address ACL-TRAFFIC
R3(config-crypto-map)#exit
Crypto Map IPv4 "CRYPTO-MAP" 11 ipsec-isakmp
Peer = 192.168.31.1
IKEv2 Profile: IKEV2-PROFILE
Extended IP access list ACL-TRAFFIC
access-list ACL-TRAFFIC permit ip 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.30.0 0.0.0.255
Current peer: 192.168.31.1
IKEV2 profile IKEV2-PROFILE
Security association lifetime: 4608000 kilobytes/3600 seconds
Responder-Only (Y/N): N
PFS (Y/N): N
Transform sets={
TRANS-set: { esp-3des esp-md5-hmac } ,
}
Applying the Crypto Map
R1(config)#interface serial 3/0
R1(config-if)#crypto map CRYPTO-MAP
R1(config-if)#exit
*Apr 1 17:15:52.575: %CRYPTO-6-ISAKMP_ON_OFF: ISAKMP is ON
R1(config)#do ping 192.168.30.1 source fa 0/0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.30.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.10.1
.!!!!
Success rate is 80 percent (4/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 52/69/92 ms
R1(config)#end
IPv4 Crypto IKEv2 SA
1 192.168.123.1/500 192.168.31.1/500 none/none READY
Encr: 3DES, Hash: SHA96, DH Grp:5, Auth sign: PSK, Auth verify: PSK
Life/Active Time: 86400/2693 sec
R3(config-if)#crypto map CRYPTO-MAP
R3(config-if)#exit
Interfaces using crypto map CRYPTO-MAP:
Serial3/1
Verify the IKEv2 IPsec
IPv4 Crypto IKEv2 Session
1 192.168.31.1/500 192.168.123.1/500 none/none READY
Encr: 3DES, Hash: SHA96, DH Grp:5, Auth sign: PSK, Auth verify: PSK
Life/Active Time: 86400/2923 sec
Child sa: local selector 192.168.30.0/0 - 192.168.30.255/65535
remote selector 192.168.10.0/0 - 192.168.10.255/65535
ESP spi in/out: 0xCF0FA2FE/0x5AAC2F32
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 100, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.30.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.10.1
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (100/100), round-trip min/avg/max = 52/63/112 ms
R1#show crypto ipsec sa
Crypto map tag: CRYPTO-MAP, local addr 192.168.123.1
local ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (192.168.10.0/255.255.255.0/0/0)
remote ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (192.168.30.0/255.255.255.0/0/0)
current_peer 192.168.31.1 port 500
PERMIT, flags={origin_is_acl,}
#pkts encaps: 104, #pkts encrypt: 104, #pkts digest: 104
#pkts decaps: 104, #pkts decrypt: 104, #pkts verify: 104
#pkts compressed: 0, #pkts decompressed: 0
#pkts not compressed: 0, #pkts compr. failed: 0
#pkts not decompressed: 0, #pkts decompress failed: 0
#send errors 0, #recv errors 0
path mtu 1500, ip mtu 1500, ip mtu idb Serial3/0
current outbound spi: 0xCF0FA2FE(3473908478)
PFS (Y/N): N, DH group: none
spi: 0x5AAC2F32(1521233714)
transform: esp-3des esp-md5-hmac ,
in use settings ={Tunnel, }
conn id: 2, flow_id: 2, sibling_flags 80000040, crypto map: CRYPTO-MAP
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4184586/795)
IV size: 8 bytes
replay detection support: Y
Status: ACTIVE(ACTIVE)
spi: 0xCF0FA2FE(3473908478)
transform: esp-3des esp-md5-hmac ,
in use settings ={Tunnel, }
conn id: 1, flow_id: 1, sibling_flags 80000040, crypto map: CRYPTO-MAP
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4184586/795)
IV size: 8 bytes
replay detection support: Y
Status: ACTIVE(ACTIVE)